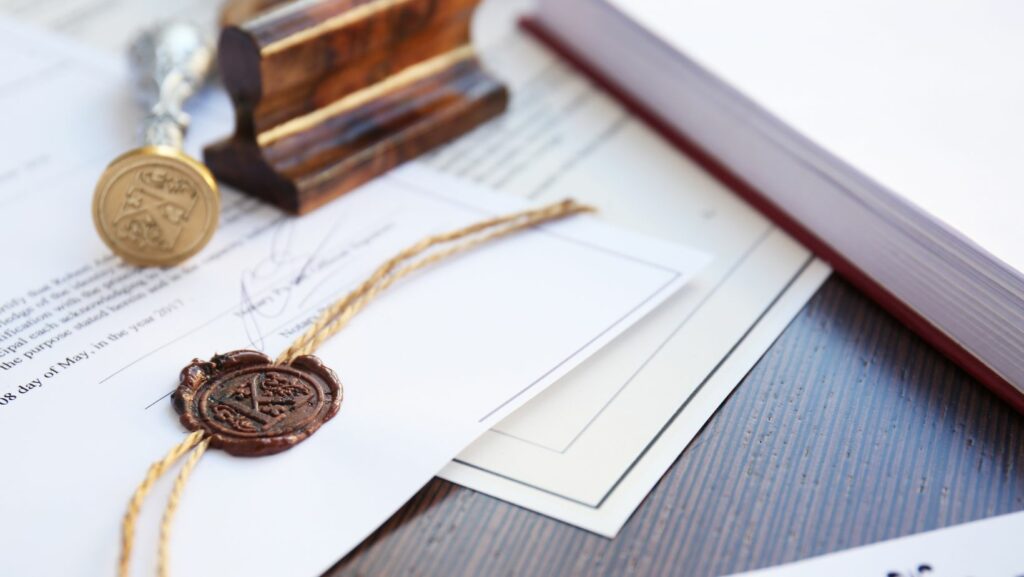
Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang Diatas Materai

When considering entering into a debt agreement or loan arrangement in Indonesia, understanding the legal requirements surrounding materai becomes crucial. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to potential disputes and challenges when seeking recourse through the legal system. Hence, grasping the nuances of this contractual element is essential for all parties involved.
In essence, surat perjanjian hutang piutang diatas materai outlines the terms and conditions of financial obligations between parties, solidifying their commitment under Indonesian law. By exploring its implications and mandates, one gains a comprehensive view of how debt and credit relationships are managed within the framework set by materai regulations.
As an expert in legal documentation, I delve into the intricate world of surat perjanjian hutang piutang diatas materai. This agreement, commonly used in Indonesia, serves as a formal contract 
Within this document, essential details such as the names of the parties involved, the amount of debt or receivable, repayment terms, and any collateral provided are explicitly stated. Surat perjanjian hutang piutang diatas materai must adhere to legal requirements and be stamped with a revenue stamp known as “materai” to validate its authenticity.
Understanding the implications of signing surat perjanjian hutang piutang diatas materai is vital to ensure both parties are aware of their rights and obligations. This legal agreement provides clarity and protection in financial transactions by establishing a formal record of the debt or receivable relationship.
Understanding Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang Diatas Materai
When it comes to Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang Diatas Materai, understanding its significance is crucial. This legal document, commonly used in financial transactions, serves as proof of 
In Indonesia, Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang Diatas Materai holds legal weight when properly executed. Parties involved must ensure that all terms and conditions are clearly outlined to prevent disputes in the future. The materai affixed to the document indicates that the necessary tax has been paid to formalize the agreement.
It’s essential for individuals and businesses entering into financial arrangements to comprehend the implications of this type of agreement. By documenting debt and receivables with Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang Diatas Materai, both lenders and borrowers can protect their interests and uphold transparency in their dealings.
Whether you’re lending money to a friend or formalizing a business loan, having a clear Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang Diatas Materai can provide security and clarity for all parties involved. Understanding the legal requirements and implications of this document is key to ensuring smooth transactions without complications down the line.
Key Components of a Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang
When drafting a Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang (debt agreement letter), it’s crucial to include key components that outline the terms and conditions of the debt settlement. These components serve as the foundation for a legally binding agreement between the creditor and debtor. Here are some essential elements to consider:
1. Parties Involved
- Clearly state the identities of both parties entering into the agreement – the creditor (pihak berhutang) and debtor (pihak berpiutang).
- Include full names, addresses, and contact information to avoid any confusion regarding the involved individuals or entities.
2. Loan Details
- Specify the amount borrowed by the debtor, including any accrued interest or additional charges.
- Outline repayment terms such as installment amounts, frequency of payments, due dates, and any penalties for late payments.
3. Interest Rates and Fees
- Define whether the loan carries a fixed or variable interest rate to provide transparency on how interest is calculated.
Mention any applicable fees like administrative charges or penalties for early repayment.
4. Collateral (if applicable)
- If collateral is provided against the loan, describe it in detail within the agreement.
- Clearly state what assets are being used as collateral and how they will be managed in case of default.
5. Dispute Resolution Mechanism
- Include provisions on how disputes related to the agreement will be resolved, whether through arbitration, mediation, or legal action.
- Establish a framework for handling disagreements to prevent potential conflicts in the future.
By incorporating these key components into a Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang, both parties can have a clear understanding of their rights and obligations concerning the debt arrangement. This structured approach not only safeguards each party’s interests but also promotes mutual trust throughout the lending process.
Legality of Materai in Loan Agreements
Exploring the LEGALITY OF MATERAI IN LOAN AGREEMENTS sheds light on an essential aspect of contractual agreements. Materai, or stamp duty, plays a crucial role in formalizing loan 
In Indonesia, for instance, materai is required for certain legal documents, including loan agreements exceeding a specified amount. Failure to affix the appropriate materai to a loan agreement could render it unenforceable in court. This underscores the significance of complying with stamp duty regulations to ensure the validity and legality of loan transactions.
Moreover, understanding the implications of materai on loan agreements involves recognizing its implications on taxation. Materai is not just a formality but also contributes to government revenue generation. By ensuring that loans are properly stamped, parties fulfill their tax obligations and contribute to the country’s fiscal resources.
In conclusion, navigating the intricacies of materai in loan agreements necessitates attention to detail and adherence to regulatory requirements. Being aware of the legal framework surrounding stamp duty can safeguard parties involved in loan transactions and uphold the integrity of contractual relationships.
Overview of Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang diatas Materai
In discussing the Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang diatas Materai, it is essential to understand its significance in formalizing debt and credit agreements. This type of agreement, commonly used in 
When delving into the specifics of this document, it becomes evident that using a stamp duty (materai) holds legal weight in validating the agreement’s authenticity. The application of materai indicates compliance with Indonesian regulations and adds a layer of enforceability to the contract.
Furthermore, parties entering into such agreements must be aware that failure to adhere to the terms outlined in the surat perjanjian can lead to legal consequences. By outlining repayment schedules, interest rates, and any collateral involved, this document serves as a crucial reference point for resolving potential disputes.
Overall, understanding the nuances of Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang diatas Materai is vital for individuals and businesses engaging in financial transactions in Indonesia. It provides a structured framework for conducting monetary dealings while offering legal protection for all involved parties.
Importance of Using Materai in Debt and Credit Agreements
When it comes to debt and credit agreements, the use of materai holds significant importance in Indonesia. Materai, or stamp duty, is a form of taxation that serves as proof that a legal document has been duly executed. Here are several reasons why utilizing materai in these agreements is crucial:
- Legal Validity: Materai ensures the legal validity of the contract. By affixing materai to the agreement, both parties acknowledge their commitment and consent to the terms outlined.
- Enforceability: A debt or credit agreement without materai may face challenges when it comes to enforceability. Materai acts as evidence that the agreement is binding and can be enforced by law if necessary.
- Prevention of Disputes: Including materai helps prevent disputes regarding the terms and conditions of the agreement. It provides clarity on the obligations of each party and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings.
- Compliance with Regulations: In Indonesia, certain agreements are required by law to be stamped with materai based on specific denominations. Failing to comply with this regulation can result in legal consequences.
In summary, incorporating materai into debt and credit agreements not only ensures their legality but also strengthens their enforceability while reducing potential disputes between parties involved. It’s an essential step in aligning with Indonesian regulations and safeguarding the interests of all parties participating in such agreements.
Key Components of a Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang
When crafting a Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang, certain essential components must be included to ensure clarity and legal validity.
Firstly, the document should clearly outline the identities of both parties involved in the agreement. This includes their full names, addresses, and other pertinent contact information. 
Next, a detailed description of the loan amount or debt owed must be provided. This should encompass specific figures, currencies involved, any interest rates applicable, and the agreed-upon repayment schedule. Clarity on these financial aspects helps prevent misunderstandings down the line.
Moreover, terms and conditions governing the agreement need to be explicitly stated. These may cover late payment penalties, default consequences, dispute resolution mechanisms, and any collateral involved. By outlining these factors comprehensively, both parties can operate within defined boundaries.
Furthermore, it’s imperative to include clauses regarding early repayment options or modifications to the agreement. Flexibility is key in ensuring that unforeseen circumstances can be addressed without jeopardizing the overall integrity of the Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang.
Lastly but significantly, obtaining signatures from all parties involved along with witnesses’ signatures adds a layer of authenticity and legal recognition to the document. Notarizing the agreement further solidifies its validity under applicable laws and regulations.
By incorporating these key components into a Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang diligently prepared by legal professionals ensures that both parties are protected and obligations are clearly delineated for mutual benefit.
Difference Between Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang and Regular Agreements
When considering the disparities between a Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang (debt acknowledgment agreement) and regular agreements, it’s crucial to note the specific legal implications each type carries. In essence, a Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang is primarily utilized for documenting debt transactions in Indonesia. While similarities exist with conventional agreements, such as 
One significant variance lies in the focus of these documents. A Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang predominantly emphasizes the borrowing and lending aspects between parties, detailing the amount borrowed, repayment terms, interest rates if applicable, and consequences for default. On the other hand, regular agreements encompass a broader spectrum of arrangements beyond debts, including partnerships, sales contracts, or service provisions.
Moreover, another differentiating factor is the statutory requirement for stamp duty on Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang in Indonesia. This mandatory stamping serves as evidence of the agreement’s legality and may vary based on the loan amount. In contrast, while regular agreements may also necessitate stamping depending on their nature and value, it is not as uniformly mandated across all types of agreements.
Additionally, enforcement mechanisms distinguish these two document categories. For instance,
- If a debtor defaults on payments stipulated in a Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang,
Legal recourse options available to creditors may be more streamlined compared to general agreements.
- Conversely,
- Disputes arising from standard contracts might involve varied resolution procedures tailored to specific contractual breaches or violations.
Understanding these disparities illuminates why clarity regarding which type of agreement suits a particular transaction scenario is paramount when formalizing financial obligations or business arrangements in Indonesia. By recognizing nuances inherent to each document category,
- Parties can ensure compliance with relevant regulations
- Safeguard their interests effectively within legal frameworks unique to debt acknowledgments versus general contractual engagements.
Signing and Notarizing the Surat Perjanjian Hutang Piutang
When it comes to finalizing a surat perjanjian hutang piutang diatas materai, SIGNING and NOTARIZING play crucial roles in ensuring its legality and enforceability. Let’s delve into what these steps entail:
- Signing Process: Before signing the agreement, all parties involved should thoroughly review the terms and conditions outlined in the surat perjanjian hutang piutang. It’s essential to ensure that everyone understands their obligations and rights as stated in the document.
- Notarizing Procedure: NOTARIZING involves a certified notary public who verifies the identities of the signatories, confirms their willingness to enter into the agreement voluntarily, and witnesses their signatures. This step adds an extra layer of authenticity to the document.
- Legal Implications: By SIGNING and NOTARIZING the surat perjanjian hutang piutang, parties demonstrate their commitment to honoring the debt or repayment terms specified. In case of disputes or legal proceedings in the future, a properly executed agreement can serve as concrete evidence.
- Enforcement Importance: A signed and notarized surat perjanjian hutang piutang holds more weight in court than an informal verbal agreement. It helps protect both creditors and debtors by establishing clear expectations and consequences for non-compliance.

 Mention any applicable fees like administrative charges or penalties for early repayment.
Mention any applicable fees like administrative charges or penalties for early repayment.
 Legal recourse options available to creditors may be more streamlined compared to general agreements.
Legal recourse options available to creditors may be more streamlined compared to general agreements.