Farmers Believed that Their Plight Derived from Which of the Following?
When exploring the causes of the farmer’s plight, it is clear that they believed their struggles stemmed from a multitude of factors. As an expert in this field, I’ll delve into some of the main reasons that farmers attributed to their challenges.
One significant factor that farmers often pointed to was fluctuating commodity prices. The agricultural market is highly volatile, and variations in supply and demand can have a profound impact on crop prices. Farmers faced uncertainty as they tried to predict and adapt to these price fluctuations, which could directly affect their profitability.
Another issue frequently cited by farmers was the burden of mounting debt. Agriculture is a capital-intensive industry, requiring substantial investments in equipment, land, and inputs. Many farmers found themselves trapped in a cycle of borrowing money to cover expenses during lean years or invest in new technologies, only to struggle with repayment when yields were low or prices dropped.
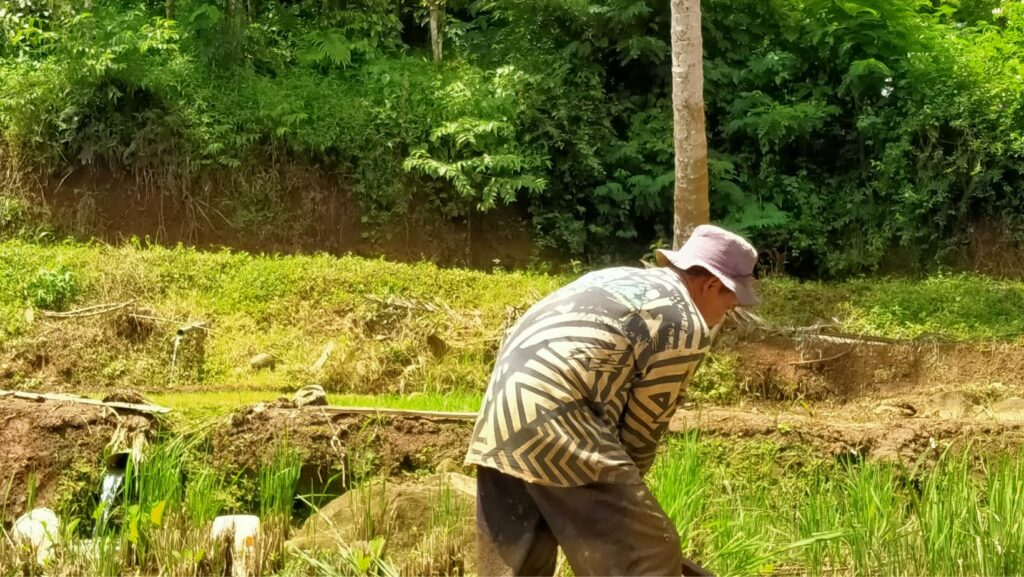
Additionally, unfavorable weather conditions played a significant role in exacerbating the farmer’s plight. Droughts, floods, pests, and other natural disasters posed constant threats to crop production. These unpredictable events could devastate entire harvests, leaving farmers without income and struggling to recover.
By understanding these key causes that farmers believed contributed to their difficulties – including fluctuating commodity prices, mounting debt burdens, and adverse weather conditions – we can gain valuable insights into the challenges they faced during this time period.

Economic Factors Affecting Farmers
When it comes to the plight of farmers, there are several economic factors that play a significant role. These factors can have a direct impact on their livelihoods and overall financial well-being. Let’s delve into some of the key economic challenges faced by farmers:
- Fluctuating Market Prices: Farmers often struggle with unpredictable market prices for their crops or livestock. The prices can vary due to various factors such as supply and demand, global trade policies, and changing consumer preferences. This volatility makes it challenging for farmers to plan their production and anticipate profits accurately.
- Rising Input Costs: Another major concern for farmers is the increasing cost of inputs like seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, machinery, and fuel. As these costs continue to rise, it becomes harder for farmers to maintain profitability while ensuring sustainable agricultural practices.
- Limited Access to Credit: Access to credit is crucial for farmers who need capital for purchasing equipment, seeds, or expanding their operations. However, many small-scale farmers face difficulties in obtaining loans from financial institutions due to lack of collateral or limited credit history.
- Weather-related Risks: Agriculture heavily relies on weather conditions, making farmers vulnerable to natural disasters such as droughts, floods, storms, or extreme temperatures. Crop failures caused by adverse weather events can lead to substantial financial losses for farmers.
- Global Market Competition: In an interconnected world economy, local farmers often face fierce competition from large-scale commercial farms abroad that benefit from economies of scale and lower production costs. This competition can put additional pressure on domestic farmers who may struggle to compete in terms of pricing and productivity.
These economic factors create immense challenges for farmers trying to sustain themselves and support their families through agriculture. It’s essential for policymakers and stakeholders in the agricultural sector to address these issues effectively by implementing supportive policies such as price stabilization mechanisms, access-to-credit programs tailored for small-scale farming operations, and risk management strategies.
By acknowledging and finding solutions to these economic challenges, we can help create a more sustainable and resilient agricultural sector that ensures the well-being of farmers and the availability of safe and affordable food for all. Agricultural practices and technologies play a crucial role in shaping the plight of farmers. Over time, advancements in farming techniques and the adoption of new technologies have brought both benefits and challenges to agricultural communities. In this section, we’ll delve into some key aspects that contribute to the struggles faced by farmers.
One major factor is the intensification of agricultural practices. With a growing population and increasing demand for food, farmers have had to ramp up production to meet the needs of society. This has led to the widespread use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). While these practices have helped increase yields, they also come with their own set of problems. Excessive use of chemicals can degrade soil health, pollute water sources, harm beneficial insects and wildlife, and potentially impact human health as well.
Another challenge arises from the reliance on monoculture cropping systems. In an effort to maximize productivity and streamline operations, many farmers have focused on cultivating a single crop over large areas of land. However, this practice leaves crops vulnerable to pests, diseases, and climate change impacts. A disease outbreak or unfavorable weather conditions can devastate entire harvests, leading to financial losses for farmers.