This comprehensive article delves into the role of facial recognition technology in finding missing children, highlighting its evolution, applications, and the ethical challenges it presents. Aimed at a broad audience, including technologists, policymakers, and child safety advocates, it provides insights into how this technology aids in child rescue efforts while also discussing the complexities of privacy, consent, and biases inherent in such systems. Readers will gain an understanding of both the technological advancements and the critical ethical considerations involved, making it a valuable resource for anyone interested in the intersection of technology, ethics, and child safety.
Understanding Facial Recognition Technology and Its Application in Child Safety
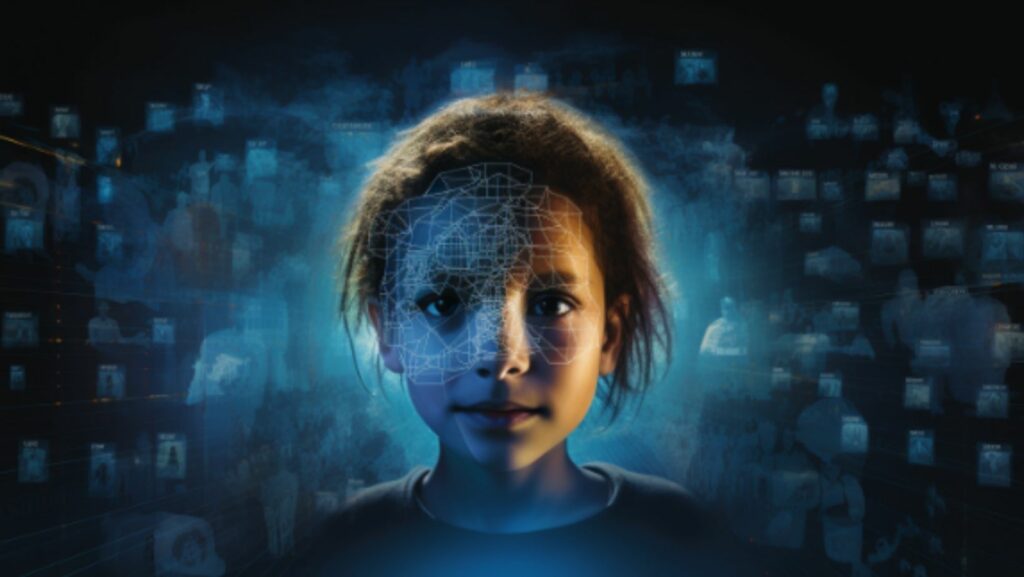
Facial recognition technology, a marvel of modern computing, maps facial features from a photograph or video and compares this information with a database of known faces. Essentially, it translates facial details into a digital formula that can be rapidly matched against a vast array of stored images. In the realm of child safety, this technology has opened new avenues for locating missing children.
Facial recognition systems are increasingly integrated into free people search platforms, enhancing the ability to scan through public records, social media, and surveillance footage. When a child goes missing, their images can be swiftly cross-referenced across these databases, significantly narrowing the search area and improving the chances of a timely reunion. This technology, once a staple of science fiction, has become a crucial tool in the fight against child disappearances, showcasing how cutting-edge innovation can serve a deeply humanitarian purpose.
From Early Concepts to Advanced Technology
The evolution of facial recognition technology is a journey from rudimentary beginnings to sophisticated, life-saving tools. It’s a tale of technological ingenuity directly impacting child safety measures.
- Initial Developments: The roots trace back to the 1960s, with systems that required manual input of facial features.
- Digital Revolution: The 1980s and 1990s saw significant advancements with the onset of digital imaging and computing power.
- 3D Facial Recognition: Introduced in the 2000s, it added depth perception, improving accuracy over the traditional 2D methods.
- Real-Time Identification: Modern systems can identify faces in real-time from live footage, vastly improving the response time in critical situations.
- Integration with Social Media: Current technologies incorporate ways to track down social media accounts of people. This includes analyzing images across platforms to identify missing children quickly.
- Machine Learning and AI: The latest advancements involve AI algorithms, making facial recognition more efficient and adaptable to various scenarios, especially in complex child safety cases.
Each step in this progression has made facial recognition more reliable and applicable in real-world situations, particularly in swiftly locating missing children.
Technological Mechanisms and Practical Applications
Facial recognition technology in finding missing children involves several key processes. Initially, the system captures an image of a child’s face, either from a photo or video. This image is then analyzed to identify unique facial features, such as the distance between the eyes or the shape of the chin. These characteristics are converted into a digital facial signature, which is compared against a database of known faces. The success of a match depends on the quality and recency of the images and the sophistication of the algorithms used.

In real-world applications, this technology has demonstrated its utility. A notable example is the case in India, where the New Delhi police used facial recognition software to trace nearly 3,000 missing children in just four days. Similarly, in the United States, the National Center for Missing & Exploited Children (NCMEC) works with technology companies to utilize facial recognition in identifying and rescuing children from exploitation and abduction scenarios.
These cases underscore the effectiveness of facial recognition in bridging the gap between disappearance and discovery, offering a crucial tool in the global fight against child abduction and trafficking. The technology not only expedites the search process but also enhances the accuracy of matches, revolutionizing how missing children cases are approached and solved.
Navigating the Complexities of Technology and Privacy
Utilizing facial recognition technology in the search for missing children brings forth a complex array of ethical considerations and privacy concerns. This intersection of technology and individual rights demands a careful balance.
- Consent and Usage: The primary ethical dilemma revolves around consent. Can a minor give consent, and how does one balance the urgent need to find a missing child with respecting individual rights?
- Data Security: Storing facial data raises significant privacy concerns. Ensuring robust protection against data breaches is paramount to maintaining trust in the technology.
- False Positives and Bias: The risk of false positives and inherent biases in the technology can lead to wrongful identifications, posing ethical and legal challenges.
- Legal Compliance: Compliance with international and national privacy laws, such as GDPR in Europe, is crucial. These laws dictate the extent to which facial recognition can be employed.
- Public Surveillance: There’s an ongoing debate over the use of facial recognition in public spaces, weighing the benefits of child safety against the broader implications for societal privacy.
Navigating these complexities requires a collaborative approach involving lawmakers, technologists, and child safety experts. Establishing clear guidelines and continuously evaluating the ethical and privacy implications are essential steps in responsibly harnessing facial recognition technology for child safety.
Emerging Innovations and Ongoing Debates
The future of facial recognition technology in the context of child safety is both promising and fraught with challenges. As advancements continue, they open new possibilities and debates in this critical field.
- Enhanced Accuracy with AI: Future developments are expected to integrate more advanced AI, improving accuracy in diverse populations and reducing false positives.
- Real-Time Processing: Innovations aim for real-time processing capabilities, enabling quicker responses in urgent missing child cases.
- Age Progression Technology: Combining facial recognition with age progression algorithms can help identify children who have been missing for extended periods.
- Cross-Platform Integration: Efforts are underway to integrate facial recognition across various platforms, including social media and public surveillance systems, for comprehensive coverage.
- Ethical AI and Bias Reduction: Ongoing research focuses on developing ethical AI systems that reduce inherent biases in facial recognition software.
- Privacy-Preserving Techniques: Innovations in privacy-preserving facial recognition methods are crucial to address growing privacy concerns while maintaining the effectiveness of child safety efforts.
These emerging innovations underscore the dynamic nature of facial recognition technology. However, each advancement brings its own set of challenges, necessitating ongoing discussions and adaptations to ensure the technology not only advances in capability but also aligns with ethical and privacy standards in child safety.
Conclusion
Facial recognition technology has evolved into a vital tool for locating missing children, blending technological innovation with humanitarian objectives. While its advancements, from early manual systems to AI-enhanced accuracy, have significantly improved child safety efforts, this progress is not without its complexities. Ethical dilemmas around consent, privacy concerns, and potential biases present ongoing challenges. Future developments, including real-time processing, age progression algorithms, and cross-platform integration, promise to enhance the technology’s efficacy. However, these advancements must be navigated with a keen awareness of privacy and ethical standards.

Collaborative efforts among technologists, legislators, and child safety experts are crucial to ensure that this powerful tool serves its noble purpose while respecting individual rights and societal values. The journey of facial recognition in child safety is a testament to human ingenuity and a reminder of our responsibility toward ethical technology deployment.